What is “oxidative stress”?
February 26, 2021
What is “oxidative stress”?
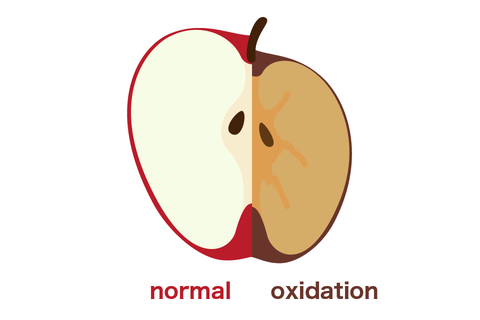
Oxidation and reduction reactions are chemical reactions that occur quite naturally in the bodies of organisms such as humans that consume oxygen to generate energy for their activities.
Currently, the following four types of oxygen are known to exist.
Superoxide
Hydroxyl radicals
Hydrogen peroxide
singlet oxygen
In the case of humans and other mammals, the majority of oxidative stress is thought to be caused by hydroxyl radicals, which readily associate with all kinds of substances such as proteins, fats, and carbohydrates to accumulate damage to the body.
A representative example is the white blood cells that act as the body’s defense force. After activating oxygen, the white blood cells convert it into hydrogen peroxide. From there, they produce “hypochlorous acid” and “hydrogen peroxide”.
These two substances are highly reactive and easily produce hydroxyl radicals. Their oxidizing power is so strong that they can oxidize, or rust, bacteria and viruses at once.
That is why they are used for disinfection and prevention of norovirus. These “highly oxidizing substances” are produced in the body.
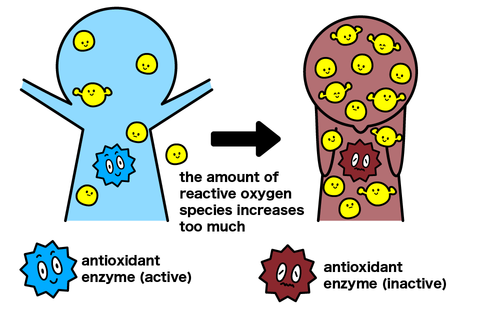
Even though hydroxyl radicals are produced, the body also has an “antioxidant system” to eliminate their harmful effects. As long as there is a balance between the oxidizing effect and the body’s own antioxidant system, it is not a big problem.
However, we are surrounded by factors that increase the production of reactive oxygen species, such as ultraviolet rays, smoking, and automobile exhaust. Whether it is mental or physical stress, consuming large amounts of alcohol, or eating too much sugar, the amount of reactive oxygen species increases.
Then, the bad side of reactive oxygen species will come out, and the body will be exposed to oxidative stress. This is not a good thing, as it can accelerate aging and increase the risk of various diseases. We should try to live a life that reduces the effects of oxidative stress as much as possible.

